lv segments on echo | 17 wall segments echo lv segments on echo Generalists most commonly request an echo to assess left ventricular (LV) dysfunction, to rule out the heart as a thromboembolic source, and to . $40.99
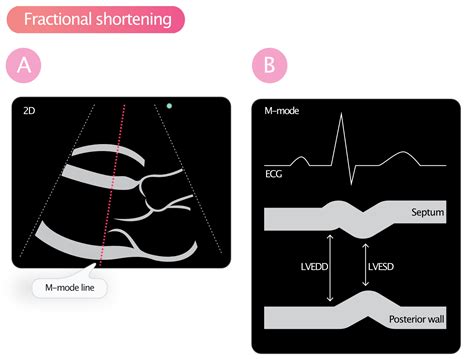
0 · what is fractional shortening echo
1 · normal lv size and function
2 · lv wall thickness echo
3 · lv wall segments echo
4 · left ventricular segmentation diagram
5 · how to assess lv function
6 · 17 wall segments echo
7 · 17 segments of the heart
Check out our two pocket business card holder selection for the very best in unique or custom, handmade pieces from our home & living shops.
The left ventricle is divided into 17 segments for 2D echocardiography. One can identify these segments in multiple views. The basal part is divided into six .Herein we review the conventional assessment of LV systolic function and examine the role of speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE), a new method .Although certain variability exists in the coronary artery blood supply to myocardial segments, segments are usually attributed to the three major coronary arteries. Visual Assessment Semi .Generalists most commonly request an echo to assess left ventricular (LV) dysfunction, to rule out the heart as a thromboembolic source, and to .
The American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) 17-segment model is an important echocardiographic framework used to describe the anatomical segments of the left and right ventricles. This model is used for .2-dimensional (2-D) echocardiography (Figure 2A) can be performed in the para-sternal long- and short-axis views by placing the calipers perpendicular to the ventricular long axis. Change in .
The LV is divided into 3 sections: base, mid-cavity, and apex; and further subdivided into 17-segments: 6 basal segments, 6 mid-cavity segments, 4 apical segments, and the true apex as . phases of relaxation = isovolumetric relaxation, early filling, diastasis (when LA passively fills LV and then stops), atrial contraction; diastolic dysfunction = disorder of LV filling .This chapter demonstrates left chamber quantification through various measurements of left ventricular size and dimensions, left ventricular mass, left ventricularglobal function, regional . Boundary identification of left ventricle (LV) in 2D echo, i.e., image segmentation, is the first step to calculate relevant clinical parameters. Currently, LV segmentation in 2D echo .
The left ventricle is divided into 17 segments for 2D echocardiography. One can identify these segments in multiple views. The basal part is divided into six segments of 60° each. The segments along the circumference are basal anterior, basal anteroseptal, basal inferoseptal, basal inferior, basal inferolateral, and basal anterolateral.Herein we review the conventional assessment of LV systolic function and examine the role of speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE), a new method to assess LV function. We also highlight the role of STE in the assessment and management of cardiac and noncardiac disease, including detection of subclinical LV dysfunction.Although certain variability exists in the coronary artery blood supply to myocardial segments, segments are usually attributed to the three major coronary arteries. Visual Assessment Semi quantitative wall motion score (1-4) can be assigned to each segment to .Generalists most commonly request an echo to assess left ventricular (LV) dysfunction, to rule out the heart as a thromboembolic source, and to characterize murmurs. The approximate normal values for various cardiac structures are described in Table 1 .
The American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) 17-segment model is an important echocardiographic framework used to describe the anatomical segments of the left and right ventricles. This model is used for assessing and reporting the regional wall motion and contractility of the ventricles.
what is fractional shortening echo
normal lv size and function
2-dimensional (2-D) echocardiography (Figure 2A) can be performed in the para-sternal long- and short-axis views by placing the calipers perpendicular to the ventricular long axis. Change in LV cavity dimensions during systole can be used to calculate .The LV is divided into 3 sections: base, mid-cavity, and apex; and further subdivided into 17-segments: 6 basal segments, 6 mid-cavity segments, 4 apical segments, and the true apex as segment 17. The 17 segments correspond to specific coronary artery territories (1).

phases of relaxation = isovolumetric relaxation, early filling, diastasis (when LA passively fills LV and then stops), atrial contraction; diastolic dysfunction = disorder of LV filling where LV is unable to fill to a normal LVEDV without an increase in end-diastolic pressure.
This chapter demonstrates left chamber quantification through various measurements of left ventricular size and dimensions, left ventricular mass, left ventricularglobal function, regional wall motion, left ventricular segmentation, global left ventricular . Boundary identification of left ventricle (LV) in 2D echo, i.e., image segmentation, is the first step to calculate relevant clinical parameters. Currently, LV segmentation in 2D echo is primarily conducted semi-manually. A fully-automatic .The left ventricle is divided into 17 segments for 2D echocardiography. One can identify these segments in multiple views. The basal part is divided into six segments of 60° each. The segments along the circumference are basal anterior, basal anteroseptal, basal inferoseptal, basal inferior, basal inferolateral, and basal anterolateral.
Herein we review the conventional assessment of LV systolic function and examine the role of speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE), a new method to assess LV function. We also highlight the role of STE in the assessment and management of cardiac and noncardiac disease, including detection of subclinical LV dysfunction.Although certain variability exists in the coronary artery blood supply to myocardial segments, segments are usually attributed to the three major coronary arteries. Visual Assessment Semi quantitative wall motion score (1-4) can be assigned to each segment to .Generalists most commonly request an echo to assess left ventricular (LV) dysfunction, to rule out the heart as a thromboembolic source, and to characterize murmurs. The approximate normal values for various cardiac structures are described in Table 1 .
The American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) 17-segment model is an important echocardiographic framework used to describe the anatomical segments of the left and right ventricles. This model is used for assessing and reporting the regional wall motion and contractility of the ventricles.2-dimensional (2-D) echocardiography (Figure 2A) can be performed in the para-sternal long- and short-axis views by placing the calipers perpendicular to the ventricular long axis. Change in LV cavity dimensions during systole can be used to calculate .The LV is divided into 3 sections: base, mid-cavity, and apex; and further subdivided into 17-segments: 6 basal segments, 6 mid-cavity segments, 4 apical segments, and the true apex as segment 17. The 17 segments correspond to specific coronary artery territories (1).
phases of relaxation = isovolumetric relaxation, early filling, diastasis (when LA passively fills LV and then stops), atrial contraction; diastolic dysfunction = disorder of LV filling where LV is unable to fill to a normal LVEDV without an increase in end-diastolic pressure.This chapter demonstrates left chamber quantification through various measurements of left ventricular size and dimensions, left ventricular mass, left ventricularglobal function, regional wall motion, left ventricular segmentation, global left ventricular .

lv wall thickness echo

lv 1002
The Already Overseas policy has a wait period of 72 hours. The 72 hour wait period starts from the date that is shown on your certificate of insurance. During the 72 hour wait period there is no cover provided under any section of the policy. That means that if you sustained an injury or become unwell within the waiting period, you won’t be .
lv segments on echo|17 wall segments echo