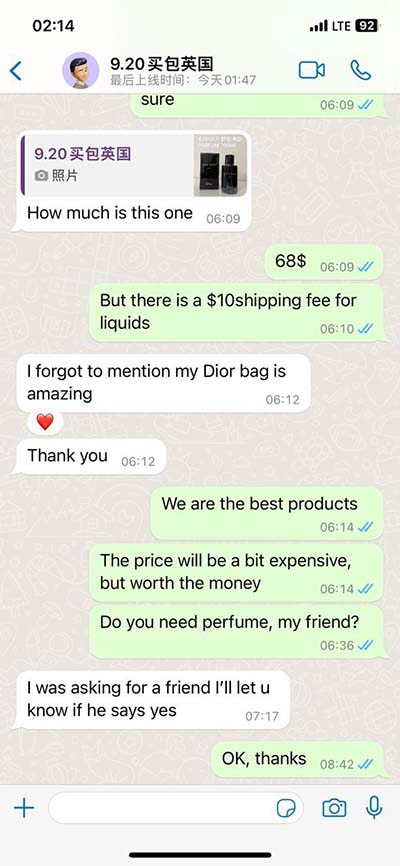
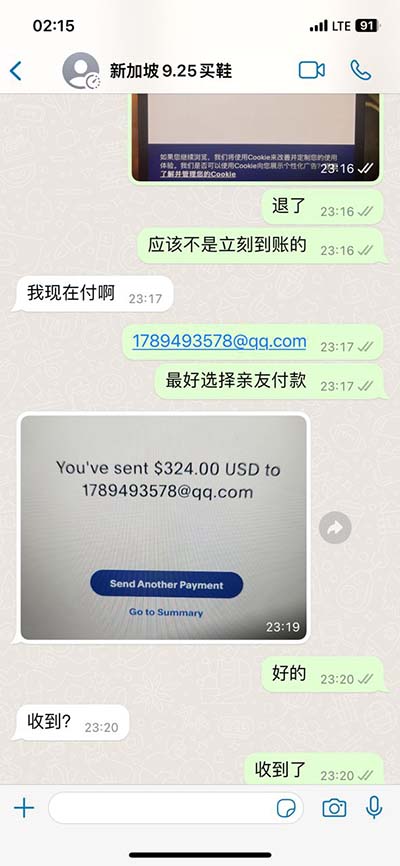
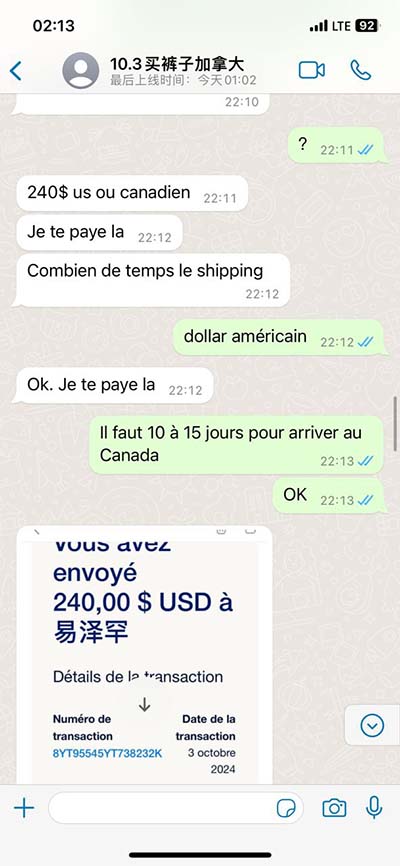
lv delete command in linux | remove a disk from lvm lv delete command in linux Step 1: Delete entry from /etc/fstab. # cat /etc/fstab. . /dev/CVOL/workspace /data ext4 defaults 0 0. . Step 2: unmount the partition. # umount /data. Step 3: Disable LVM. # . 2 Beds 2 Bath Apartments in Las Vegas, NV | Capri North and South. B AVAILABILITY. Home / FLOOR PLANS / B. BED: 2. BATH: 2. SQ. FEET: 940. Our apartment homes offer: spacious residences feature fireplaces, over-sized garden tubs, large walk-in closets, washers and dryers and covered parking. *This rate does not include the technology .
0 · remove a disk from lvm
1 · lvremove logical volume in use
2 · lvremove command in Linux
3 · lvm remove disk from vg
4 · how to delete lvm partition
5 · how to delete an lvm
6 · delete volume group Linux
7 · delete vg in Linux
125 talking about this
To remove an inactive logical volume, use the lvremove command. If the logical volume is currently mounted, unmount the volume before removing it. In addition, in a . The `lvremove` command is used to remove one or more logical volumes. It is a part of the LVM (Logical Volume Manager) system, which allows for the management of disk .
Step 1: Delete entry from /etc/fstab. # cat /etc/fstab. . /dev/CVOL/workspace /data ext4 defaults 0 0. . Step 2: unmount the partition. # umount /data. Step 3: Disable LVM. # . Remove a logical volume. The command lvremove can be used to remove logical volumes. We should make sure a logical volume does not have any valuable data stored on it .lvremove Command Examples. 1. To remove the logical volume: # lvremove LV00. 2. To forcefully remove the logical volume: # lvremove -f LV00.
Removing a logical volume. A logical volume must be closed before it can be removed: # umount /dev/myvg/homevol # lvremove /dev/myvg/homevollvremove -- do you really want to remove . In this comprehensive guide, we’ve delved into the world of the LVM command in Linux, a powerful tool for managing disk drives in Linux. We’ve covered the basic to advanced . To remove a Physical Volume first we need to remove it from the Volume group using below syntax. Syntax: # vgreduce name_of_vol_grp path/of/pv. # vgreduce VolGroup .
You can use lvremove command to remove the specified logical volume in the volume group. For example, the following command removes the logical volume lvol1 in the volume group vol_grp . $ sudo lvremove vol_grp/lvol1 To remove an inactive logical volume, use the lvremove command. If the logical volume is currently mounted, unmount the volume before removing it. In addition, in a clustered environment you must deactivate a logical volume before it can be removed. The `lvremove` command is used to remove one or more logical volumes. It is a part of the LVM (Logical Volume Manager) system, which allows for the management of disk space on Linux systems. By using `lvremove`, logical volumes can be deleted, freeing up disk space and effectively removing any data stored within them.
Delete Logical Volume (LVM) in Linux. 1. Check Logical Volume. 2. Unmount the Volume using umount command. 3. Disable Logical Volume using lvchange command. 4. Delete Logical Volume using lvremove command. Advertisements. In this article, I will take you through the steps to disable or delete Logical Volume in Linux.

remove a disk from lvm
Step 1: Delete entry from /etc/fstab. # cat /etc/fstab. . /dev/CVOL/workspace /data ext4 defaults 0 0. . Step 2: unmount the partition. # umount /data. Step 3: Disable LVM. # lvchange -an /dev/CVOL/workspace. Step 4: Delete LVM volume. Remove a logical volume. The command lvremove can be used to remove logical volumes. We should make sure a logical volume does not have any valuable data stored on it before we attempt to remove it. Moreover, we should make sure the volume is not mounted. # lvremove /dev/mynew_vg/vol02lvremove Command Examples. 1. To remove the logical volume: # lvremove LV00. 2. To forcefully remove the logical volume: # lvremove -f LV00.Removing a logical volume. A logical volume must be closed before it can be removed: # umount /dev/myvg/homevol # lvremove /dev/myvg/homevollvremove -- do you really want to remove "/dev/myvg/homevol"? [y/n]: ylvremove -- doing automatic backup of volume group "myvg" lvremove -- logical volume "/dev/myvg/homevol" successfully removed. Prev.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve delved into the world of the LVM command in Linux, a powerful tool for managing disk drives in Linux. We’ve covered the basic to advanced usage of LVM, its core functionality, and solutions to common issues. To remove a Physical Volume first we need to remove it from the Volume group using below syntax. Syntax: # vgreduce name_of_vol_grp path/of/pv. # vgreduce VolGroup /dev/sdb1. Removed "/dev/sdb1" from volume group "VolGroup". Once reduce from volgroup we can easily remove the PV using below command.
You can use lvremove command to remove the specified logical volume in the volume group. For example, the following command removes the logical volume lvol1 in the volume group vol_grp . $ sudo lvremove vol_grp/lvol1
To remove an inactive logical volume, use the lvremove command. If the logical volume is currently mounted, unmount the volume before removing it. In addition, in a clustered environment you must deactivate a logical volume before it can be removed. The `lvremove` command is used to remove one or more logical volumes. It is a part of the LVM (Logical Volume Manager) system, which allows for the management of disk space on Linux systems. By using `lvremove`, logical volumes can be deleted, freeing up disk space and effectively removing any data stored within them. Delete Logical Volume (LVM) in Linux. 1. Check Logical Volume. 2. Unmount the Volume using umount command. 3. Disable Logical Volume using lvchange command. 4. Delete Logical Volume using lvremove command. Advertisements. In this article, I will take you through the steps to disable or delete Logical Volume in Linux. Step 1: Delete entry from /etc/fstab. # cat /etc/fstab. . /dev/CVOL/workspace /data ext4 defaults 0 0. . Step 2: unmount the partition. # umount /data. Step 3: Disable LVM. # lvchange -an /dev/CVOL/workspace. Step 4: Delete LVM volume.
Remove a logical volume. The command lvremove can be used to remove logical volumes. We should make sure a logical volume does not have any valuable data stored on it before we attempt to remove it. Moreover, we should make sure the volume is not mounted. # lvremove /dev/mynew_vg/vol02lvremove Command Examples. 1. To remove the logical volume: # lvremove LV00. 2. To forcefully remove the logical volume: # lvremove -f LV00.Removing a logical volume. A logical volume must be closed before it can be removed: # umount /dev/myvg/homevol # lvremove /dev/myvg/homevollvremove -- do you really want to remove "/dev/myvg/homevol"? [y/n]: ylvremove -- doing automatic backup of volume group "myvg" lvremove -- logical volume "/dev/myvg/homevol" successfully removed. Prev. In this comprehensive guide, we’ve delved into the world of the LVM command in Linux, a powerful tool for managing disk drives in Linux. We’ve covered the basic to advanced usage of LVM, its core functionality, and solutions to common issues.

lvremove logical volume in use
Carrillo Landscape Services Inc in Las Vegas, NV | Photos | Reviews | Based in Las Vegas, ranks in the top 99% of licensed contractors in Nevada. C10 Landscape Contracting, C 10 Landscape Contracting License: 71823, 0071823.
lv delete command in linux|remove a disk from lvm