is hermes an olympian | Hermes greek mythology facts is hermes an olympian Hermes began as a god with strong chthonic, or underworld, associations. He was a psychopomp, leader of souls along the road between . See more You should try to always get an Overkill strike on a Defender Z for this reason. If you're having trouble killing them or getting an Overkill try using Auron's Armor Break. If you just want to acquire a ton of Level 3 Key Spheres really quickly the best way to do so is by bribing the Demonolith enemy Inside Sin.
0 · who are Hermes parents
1 · what powers did Hermes have
2 · olympian god Hermes facts
3 · facts about Hermes god
4 · fact about Hermes
5 · Hermes greek mythology facts
6 · Hermes greek god children
7 · Hermes facts greek god
Category:Alchemist Quests. The following is the quest line for the Alchemist class. Rebuild Lists. Name. Rewards. Patch. &0000000000000001000000 1 &0000000000066111000000 66,111 &0000000000000002000000 2.0 &0000000000000010000000 10Way of the Alchemist. Way of the Alchemist (Level. .
Hermes is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology considered the herald of the gods. He is also widely considered the protector of human heralds, travelers, thieves, merchants, and orators. He is able to move quickly and freely between the worlds of the mortal and the divine aided by his . See more
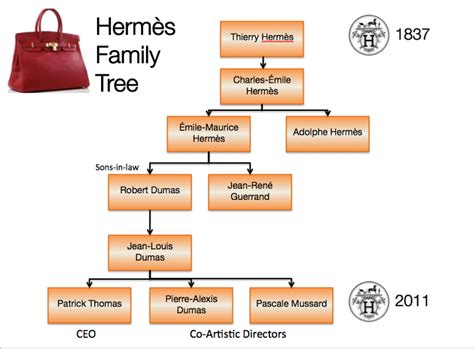
The earliest form of the name Hermes is the Mycenaean Greek *hermāhās, written 𐀁𐀔𐁀 e-ma-a2 (e-ma-ha) in the Linear B syllabic script. Most . See moreHermes began as a god with strong chthonic, or underworld, associations. He was a psychopomp, leader of souls along the road between . See moreAtlantiadesHermes was also called Atlantiades (Greek: Ατλαντιάδης), because his mother, Maia was the daughter of Atlas.ArgeïphontesHermes's epithet Argeïphontes (Ancient Greek See moreFor Carl Jung, Hermes's role as messenger between realms and as guide to the underworld made him the god of the unconscious, . See more
The image of Hermes evolved and varied along with Greek art and culture. In Archaic Greece he was usually depicted as a mature man, bearded, and dressed as a traveler, herald, or shepherd. This image remained common on the Hermai, which served as . See moreIn the Mycenaean periodThe earliest written record of Hermes comes from Linear B inscriptions from Pylos, Thebes, and Knossos dating to the Bronze Age See more
Early Greek sourcesHomer and HesiodHomer and Hesiod portrayed Hermes as the author of skilled . See more The Role of Hermes in Olympian Mythology. As a prominent figure on Mount Olympus, Hermes maintains relationships with various gods, often serving as a bridge .
Hermes’ relationships with other Olympian gods reveal much about his character and the values of Greek mythology. From his role as a messenger to his connections with .
Table of Contents. Hermes and the Olympic Games: Patron of Athletes and Competitions. I. Introduction. In the rich tapestry of Greek mythology, Hermes stands out as a . Hermes, son of Zeus, wearer of winged sandals, was one of the most important and referred to of the Olympian gods. He was the protector of the baby Dionysus, ran messages . One of the cleverest and most mischievous of the 12 Olympian gods, Hermes was their herald and messenger. In that position, he came to symbolise the crossing of boundaries in his role as a guide between the two .
Hermes was an Olympian god of travel, trade, diplomacy, persuasion, writings and athletics. He was also the messenger of gods because he could moved freely and fast between the worlds . Hermes, Greek god, son of Zeus and the Pleiad Maia; often identified with the Roman Mercury. Hermes was associated with the protection of cattle and sheep. In the . The ancient Greeks recognised him as one of the twelve Olympian gods, serving primarily as Zeus’s herald or messenger. His sacred number was four, with his birthday .Hermes (/ ˈ h ɜːr m iː z /; ‹See Tfd› Greek: Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology considered the herald of the gods. He is also widely considered the protector of human heralds, travelers, thieves, [2] merchants, and orators.
The Role of Hermes in Olympian Mythology. As a prominent figure on Mount Olympus, Hermes maintains relationships with various gods, often serving as a bridge between them. His duties as a divine messenger and mediator are . Hermes’ relationships with other Olympian gods reveal much about his character and the values of Greek mythology. From his role as a messenger to his connections with deities of love, music, revelry, and the Underworld, Hermes embodies the essence of communication, commerce, and balance. Table of Contents. Hermes and the Olympic Games: Patron of Athletes and Competitions. I. Introduction. In the rich tapestry of Greek mythology, Hermes stands out as a multifaceted figure known for his speed, cunning, and role as the messenger of the gods. One of the most famous statues of Hermes is known as the ‘Hermes of Olympia’ or the ‘Hermes of Praxiteles’, found amongst the ruins of a temple dedicated to Hera in Olympia. There is also priceless artwork depicting Hermes on .
Hermes, son of Zeus, wearer of winged sandals, was one of the most important and referred to of the Olympian gods. He was the protector of the baby Dionysus, ran messages from the underworld, and was the trickster god who gave Pandora her famous box. Among the ancient Greeks, Hermes was revered. One of the cleverest and most mischievous of the 12 Olympian gods, Hermes was their herald and messenger. In that position, he came to symbolise the crossing of boundaries in his role as a guide between the two realms of gods and humanity.
Hermes was an Olympian god of travel, trade, diplomacy, persuasion, writings and athletics. He was also the messenger of gods because he could moved freely and fast between the worlds of mortal and divine. Many thought of him as the protector of . Hermes, Greek god, son of Zeus and the Pleiad Maia; often identified with the Roman Mercury. Hermes was associated with the protection of cattle and sheep. In the Odyssey, however, he appears mainly as the messenger of the gods and the conductor of . The ancient Greeks recognised him as one of the twelve Olympian gods, serving primarily as Zeus’s herald or messenger. His sacred number was four, with his birthday believed to fall on the fourth day of the month. Celebrated for his inventions, Hermes is particularly known for creating the lyre on the day of his birth, using a tortoise shell.Hermes (/ ˈ h ɜːr m iː z /; ‹See Tfd› Greek: Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology considered the herald of the gods. He is also widely considered the protector of human heralds, travelers, thieves, [2] merchants, and orators.

The Role of Hermes in Olympian Mythology. As a prominent figure on Mount Olympus, Hermes maintains relationships with various gods, often serving as a bridge between them. His duties as a divine messenger and mediator are .
who are Hermes parents
Hermes’ relationships with other Olympian gods reveal much about his character and the values of Greek mythology. From his role as a messenger to his connections with deities of love, music, revelry, and the Underworld, Hermes embodies the essence of communication, commerce, and balance. Table of Contents. Hermes and the Olympic Games: Patron of Athletes and Competitions. I. Introduction. In the rich tapestry of Greek mythology, Hermes stands out as a multifaceted figure known for his speed, cunning, and role as the messenger of the gods.
One of the most famous statues of Hermes is known as the ‘Hermes of Olympia’ or the ‘Hermes of Praxiteles’, found amongst the ruins of a temple dedicated to Hera in Olympia. There is also priceless artwork depicting Hermes on . Hermes, son of Zeus, wearer of winged sandals, was one of the most important and referred to of the Olympian gods. He was the protector of the baby Dionysus, ran messages from the underworld, and was the trickster god who gave Pandora her famous box. Among the ancient Greeks, Hermes was revered. One of the cleverest and most mischievous of the 12 Olympian gods, Hermes was their herald and messenger. In that position, he came to symbolise the crossing of boundaries in his role as a guide between the two realms of gods and humanity.
Hermes was an Olympian god of travel, trade, diplomacy, persuasion, writings and athletics. He was also the messenger of gods because he could moved freely and fast between the worlds of mortal and divine. Many thought of him as the protector of .
Hermes, Greek god, son of Zeus and the Pleiad Maia; often identified with the Roman Mercury. Hermes was associated with the protection of cattle and sheep. In the Odyssey, however, he appears mainly as the messenger of the gods and the conductor of .

nike free run 2017 vrouwen grijs

A giant that roams the hills, subsisting on the flesh of the mighty beasts it hunts. It lives a nomadic life, always moving in search of new prey. Though generally shunning contact with others, it is nonetheless a simple and curious creature, .
is hermes an olympian|Hermes greek mythology facts