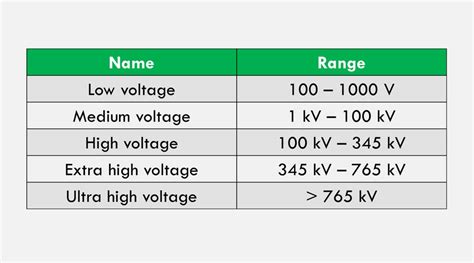
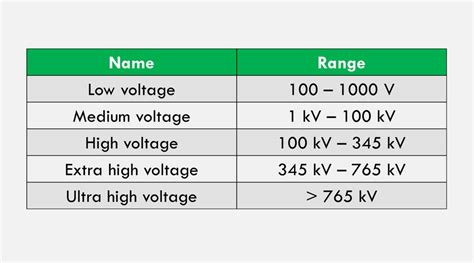
lv mv hv ehv uhv ranges in india | ehv ratings chart lv mv hv ehv uhv ranges in india As such, as per the latest Regulations in vogue in India, there is no such classifications as LV, MV, HV & EHV. The National Electric Code (of India) 2011 (Reaffirmed in 2016): Part 1 – Section 2 -Low Voltage: The voltage which does not normally exceed 250 V . Louis Vuitton Fakes: The Bag Itself. What to Do If You Buy a Louis Vuitton Fake. Where to Find Authentic Louis Vuitton Bags. Frequently Asked Questions. Louis Vuitton is one of the most famous names in fashion, and with such a stylish track record, it's no wonder so many people want to wear it.
0 · high voltage rating in india
1 · ehv voltage rating
2 · ehv ratings chart
3 · ehv rating in india
The cave incident by brainstorm1001 reviews. Three years after the lost battle of Hogwarts Lord Voldemort attempts revenge. Regrettably, he has never learned from his mistakes and underestimates Harry's incredible luck again. HPLV later. Warning: mix .
As such, as per the latest Regulations in vogue in India, there is no such classifications as LV, MV, HV & EHV. The National Electric Code (of India) 2011 (Reaffirmed in 2016): Part 1 – Section 2 -Low Voltage: The voltage which does not normally exceed 250 V .As such, as per the latest Regulations in vogue in India, there is no such .How to identify a Tower Voltage Level While using Porcelain insulator: In India, mostly porcelain insulators are used for the transmitting power. The insulator is made up of disk types and each disk has the ability to withstand up to 12kV. . The Indian Electricity Rules, 1956, the following were the voltage limits of power system and equipment −. Low Voltage (LV) − Less than or equal to 250 V. Medium Voltage .
High Voltage Range I: > 1kV but 245kV. The acronyms EHV (Extra High Voltage) and UHV (Ultra High Voltage), though are being used .It is quite common for this to be further broken down into medium voltage (MV), high voltage (HV), and extra high voltage (EHV). As we scale up, we enter the realm of medium voltage (MV), .
High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a .In this blog, we present the definition of LV, MV and HV, the differences between voltages and their usage areas and more for you. What is the definition of Low Voltage, Medium Voltage and High Voltage?
hardest rolex to get 2023
High Voltage - 35kV to 230 kV. Extra High Voltage - above 230 kV. In some situations, the term Ultra High Voltage is used to denote voltages above 800 kV. In addition, the IEC defines a .Earlier in the year 1990 Central Electricity Authority (CEA) brought out a report detailing parameters of the 800 kV class equipment and transmission line material based on the .High tension (HV/HT): below 33 KV. Extra-high-voltage (EHV) : above 33 KV. Note: The distribution Transformer designed in India is for 433V secondary terminal voltage but when it . As such, as per the latest Regulations in vogue in India, there is no such classifications as LV, MV, HV & EHV. The National Electric Code (of India) 2011 (Reaffirmed in 2016): Part 1 – Section 2 -Low Voltage: The voltage which does not .
How to identify a Tower Voltage Level While using Porcelain insulator: In India, mostly porcelain insulators are used for the transmitting power. The insulator is made up of disk types and each disk has the ability to withstand up to 12kV. Look at the image of 66kV porcelain insulator. The Indian Electricity Rules, 1956, the following were the voltage limits of power system and equipment −. Low Voltage (LV) − Less than or equal to 250 V. Medium Voltage (MV) − Less than or equal to 650 V. High Voltage (HV) − Less than 33 kV. Extra-High Voltage (EHV) − More than 33 kV. High Voltage Range I: > 1kV but 245kV. The acronyms EHV (Extra High Voltage) and UHV (Ultra High Voltage), though are being used elaborately in India, have never been officially defined in any of the above three standards. USA:It is quite common for this to be further broken down into medium voltage (MV), high voltage (HV), and extra high voltage (EHV). As we scale up, we enter the realm of medium voltage (MV), typically ranging between 1000V and 35kV, commonly used in industrial facilities. But for large-scale power transmission, high voltage (HV) is essential.
High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site Generation Overview. The white paper compares NEC to ANSI Standards.
In this blog, we present the definition of LV, MV and HV, the differences between voltages and their usage areas and more for you. What is the definition of Low Voltage, Medium Voltage and High Voltage?
High Voltage - 35kV to 230 kV. Extra High Voltage - above 230 kV. In some situations, the term Ultra High Voltage is used to denote voltages above 800 kV. In addition, the IEC defines a voltage band known as the Extra Low Voltage with a AC voltage less than 70 V. See article here.Earlier in the year 1990 Central Electricity Authority (CEA) brought out a report detailing parameters of the 800 kV class equipment and transmission line material based on the recommendations of Working Groups constituted following the decision of Government of India to select 800 kV (with 765 kV as the nominal voltage) as the next higher AC Tr.High tension (HV/HT): below 33 KV. Extra-high-voltage (EHV) : above 33 KV. Note: The distribution Transformer designed in India is for 433V secondary terminal voltage but when it comes to the load side it will be only 415 V as per standards. Similarly, all 3 phases generated and motor voltage should be 415V. As such, as per the latest Regulations in vogue in India, there is no such classifications as LV, MV, HV & EHV. The National Electric Code (of India) 2011 (Reaffirmed in 2016): Part 1 – Section 2 -Low Voltage: The voltage which does not .
How to identify a Tower Voltage Level While using Porcelain insulator: In India, mostly porcelain insulators are used for the transmitting power. The insulator is made up of disk types and each disk has the ability to withstand up to 12kV. Look at the image of 66kV porcelain insulator.
The Indian Electricity Rules, 1956, the following were the voltage limits of power system and equipment −. Low Voltage (LV) − Less than or equal to 250 V. Medium Voltage (MV) − Less than or equal to 650 V. High Voltage (HV) − Less than 33 kV. Extra-High Voltage (EHV) − More than 33 kV. High Voltage Range I: > 1kV but 245kV. The acronyms EHV (Extra High Voltage) and UHV (Ultra High Voltage), though are being used elaborately in India, have never been officially defined in any of the above three standards. USA:It is quite common for this to be further broken down into medium voltage (MV), high voltage (HV), and extra high voltage (EHV). As we scale up, we enter the realm of medium voltage (MV), typically ranging between 1000V and 35kV, commonly used in industrial facilities. But for large-scale power transmission, high voltage (HV) is essential.
High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site Generation Overview. The white paper compares NEC to ANSI Standards.
In this blog, we present the definition of LV, MV and HV, the differences between voltages and their usage areas and more for you. What is the definition of Low Voltage, Medium Voltage and High Voltage?High Voltage - 35kV to 230 kV. Extra High Voltage - above 230 kV. In some situations, the term Ultra High Voltage is used to denote voltages above 800 kV. In addition, the IEC defines a voltage band known as the Extra Low Voltage with a AC voltage less than 70 V. See article here.
Earlier in the year 1990 Central Electricity Authority (CEA) brought out a report detailing parameters of the 800 kV class equipment and transmission line material based on the recommendations of Working Groups constituted following the decision of Government of India to select 800 kV (with 765 kV as the nominal voltage) as the next higher AC Tr.
high voltage rating in india
FALB 080 = 80 W = 100 W 120 = 120 W 100 150 = 150 W 185 = 185 W 240 = 240 W Electrical Drivers: 120-277V, 50-60 Hz, Power Factor > 90% 0-10 V Dimmable (all except FALB080/ FALB100) (optional) HV of 480V SF Color Temperature Lens: Polycarbonate LED Characteristics FEATURES-Limited Warranty: 5 Years-Efficacy: up to 131 LPW .
lv mv hv ehv uhv ranges in india|ehv ratings chart